
A. What are Bleeding Patterns on HRT ?
B. Managing Bleeding problems within first 6 month of starting HRT in low risk women
C. When should you be investigated?
D. Which investigations are indicated ?
E. Progestogens and Endometrial Protection
Women with a uterus should take monthly progestogen hormone in tablet, Combined patch or Coil (Mirena /Levosert/Benelixa coil) to prevent cancer of the womb caused by estrogen. Most bleeding problems on HRT is due to HRT , but it is important to rule out other causes like sexually transmitted infections , uterine cancer or pre-cancer , cervical cancer , uterine polyps , fibroids in the cavity of Uterus , vaginal atrophy ( thin vagina due to lack of estrogen)
Some women are not taking the progestogen due to side effects or forgetting to take these tablets putting themselves at a risk of uterine cancer.
A. What are Bleeding patterns on HRT ?
There are 2 types of HRT:
1. Period HRT : is also called Sequential HRT (Seq HRT) . This includes taking estrogen continuously and progestogen for 2 weeks every month, sequence of hormones just like your own hormones released from the ovary during reproductive years . At the end of the 2 weeks you will usually have a period/bleed .
This HRT is advised for women who are still having periods even if they are irregular in the last 12 months ie in women who are perimenopausal.
Irregular bleeding is common in the first few months which usually settles.
2. No Period HRT : is also called Continuous Combined HRT (CCHRT). This includes taking estrogen and progestogen continuously. With this HRT irregular bleeding is common in the first 3-6 months which usually settles and women then have no further bleeds therefore it is called a no Bleed HRT .
This HRT is advised for women who have no periods in the preceding 12 months or those who are perimenopausal.
B. Managing Bleeding problems on HRT in first 6 months
Your doctor will take a detailed history of bleeding pattern, check your HRT regime, duration, compliance ( as some women omit the progestogen tablets due to PMS side effects), drug interactions which can reduce efficacy of HRT , poor absorption, contraception use , smear .sexual history and risk factors for uterine cancer.
Your doctor may change your HRT from patches to tablets, increase dose of progestogen , reduce dose of estrogen if its high , change from no bleed HRT to a bleed HRT or insert Hormone coil ( Mirena/Benelixa ) in the absence of risk factors for uterine cancer .
C. When should you be investigated ?
Risk of uterine cancer on HRT is low . Risk of uterine cancer is lower with No period HRT (CCHRT) compared with Period HRT (Seq HRT ) as it keeps the lining of the womb thin. After taking a period HRT for 1-2 years , your doctor will change your HRT to a no period HRT.
1. If you have risk factors for cancer of the womb such as BMI over 30, family history of uterine cancer , past history of Polycystic ovarian syndrome or Diabetes you will have a higher baseline risk of cancer . If you have a BMI over 40 (this increases risk of uterine cancer by 10 fold ) and if you have 3 risk factors for uterine cancer listed above you will be referred to gynaecology for investigations to be seen with 2 weeks to rule out cancer of the womb. 2. If you continue to bleed beyond 6 months on Sequential or CCHRT inspite of adjusting dose of HRT or have bleeding on CCHRT after being bleed free for several months . 3. Heavy Bleeds or constant bleeding on HRT 4. You take estrogen only HRT with a Uterus and omit taking progestogen 5. If you are on high doses of estrogen and progestogen dose is not in proportion, such as taking oral Estrogen 3-4 mg or Estradiol patches 100 mcg or Estrogel 5-6 pumps daily or if you have a BMI of >40, and risk factors for Uterine cancer such as Family history , PCOS or Diabetes.
D. Which investigations are recommended
You will have an abdominal and internal examination to check the cervix , swabs to check for infections .
Pelvic Ultrasound scan to check the thickness of the lining of the womb and look for presence of fibroids and polyps
In some cases, a hysteroscopy and Biopsy to rule out precancer and cancer of the womb.
E. Progestogen and Endometrial protection
Ensure progestogen dose is proportionate to oestrogen dose to prevent Uterine Cancer and unscheduled erratic bleeding on HRT.
Below is the chart on Estrogen and Progestogen dose from the British Menopause Society
Guideline on Management of Unscheduled Bleeding on HRT ( published in April 24)
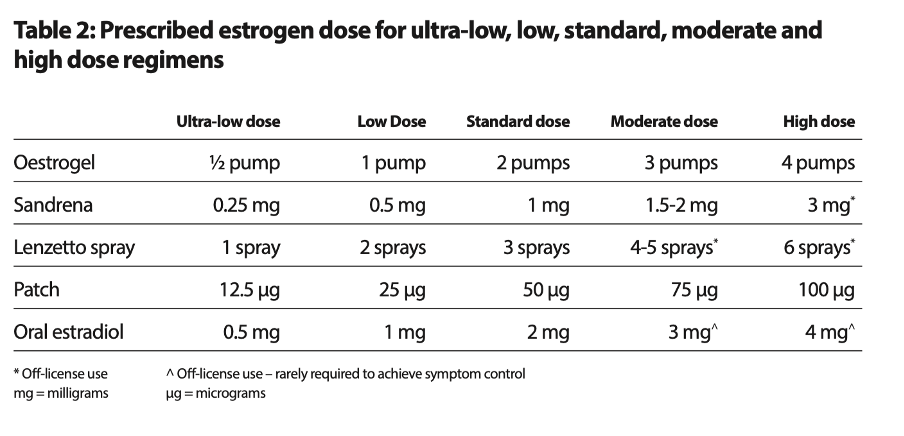
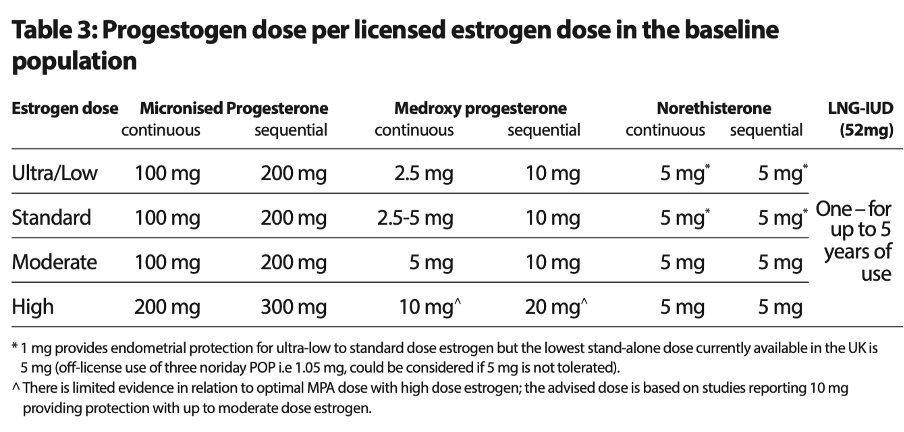
Dose of progestogen can be increased or HRT can be changed if bleeding occurs in the first 6 months of starting HRT . If bleeding doesn’t settle or women has risk factors for Uterine cancer further investigations are indicated.